Multimedia Gallery
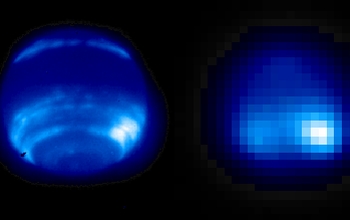
Neptune observed in the near infrared using AO
Neptune observed in the near infrared (1.65 microns) using adaptive optics (AO) (left) and without AO (right). Neptune is the outermost of the giant planets in our solar system and has the most dynamic and rapidly changing weather patterns. This near-infrared image is primarily sensitive to high-altitude clouds, which appear bright against the darker disk. AO allows ground-based telescopes to monitor Neptune's evolving weather systems and to use spectroscopy to probe different altitudes in its poorly understood atmosphere.
This research was conducted at the Center for Adaptive Optics (CfAO) at the University of California, Santa Cruz, a National Science Foundation-supported Science and Technology Center. The center researches AO in the fields of vision science and astronomy to remove the effects of image blurring through turbulent media. Applications include astronomical telescopes, laser-guide stars, wavefront sensing, microelectromechanical systems technology and retinal imaging.
Credit: Center for Adaptive Optics, UCSC
Images and other media in the National Science Foundation Multimedia Gallery are available for use in print and electronic material by NSF employees, members of the media, university staff, teachers and the general public. All media in the gallery are intended for personal, educational and nonprofit/non-commercial use only.
Images credited to the National Science Foundation, a federal agency, are in the public domain. The images were created by employees of the United States Government as part of their official duties or prepared by contractors as "works for hire" for NSF. You may freely use NSF-credited images and, at your discretion, credit NSF with a "Courtesy: National Science Foundation" notation.
Additional information about general usage can be found in Conditions.
Also Available:
Download the high-resolution TIFF version of the image. (291 KB)
Use your mouse to right-click (Mac users may need to Ctrl-click) the link above and choose the option that will save the file or target to your computer.