All Images
News Release 08-032
Ranger Supercomputer Dedicated by NSF and Texas Advanced Computing Center
Quantum leap in computational power and memory capacity for research community through the TeraGrid
This material is available primarily for archival purposes. Telephone numbers or other contact information may be out of date; please see current contact information at media contacts.

Understanding HIV drug-resistance:
A snapshot of the HIV-1 protease (a key protein that is the target for the protease inhibitor drugs) from a computational simulation. Mutations from the "wildtype" can occur within the active site (G48V) and at remote locations along the protein chain (L90M ). The "asp dyad" is at the centre of the active site, where polyprotein changes are snipped by the enzyme; this is the region that any drug must occupy and block.
Credit: Peter Coveney, University College London. Texas Advanced Computing Center.
Download the high-resolution JPG version of the image. (49 KB)
Use your mouse to right-click (Mac users may need to Ctrl-click) the link above and choose the option that will save the file or target to your computer.
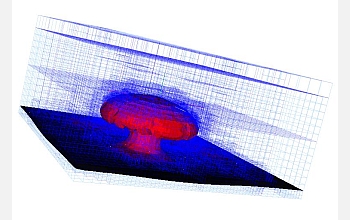
Modeling Mantle Convection:
A sequence of snapshots from a simulation of a model of the Earth's mantle showing a convection problem. Images depict rising temperature plume within the Earth's mantle, indicating the dynamically-evolving mesh required to resolve steep thermal gradients.
Credit: Simulations by Rhea Group (Carsten Burstedde, Omar Ghattas, Georg Stadler, Tiankai Tu, Lucas Wilcox), in collaboration with George Biros (Penn), Michael Gurnis (Caltech), and Shijie Zhong (Colorado). Texas Advanced Computing Center.
Download the high-resolution JPG version of the image. (74 KB)
Use your mouse to right-click (Mac users may need to Ctrl-click) the link above and choose the option that will save the file or target to your computer.


