News Release 11-015
Mathematical Model Could Help Predict and Prevent Future Extinctions
Research could rescue fragile ecosystems and halt complex cascade events
A newly developed mathematical model suggests some species extinctions can be avoided.
January 25, 2011
This material is available primarily for archival purposes. Telephone numbers or other contact information may be out of date; please see current contact information at media contacts.
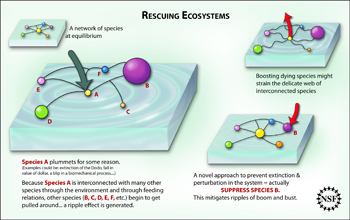
In an effort to better understand the dynamics of complex networks, scientists have developed a mathematical model to describe interactions within ecological food webs. This research, performed by Northwestern University physics professor Adilson Motter and his student, Sagar Sahasrabudhe, is published in the January 25 issue of Nature Communications. The work illustrates how human intervention may effectively aid species conservation efforts.
"Our study provides a theoretical basis for management efforts that would aim to mitigate extinction cascades in food web networks. There is evidence that a significant fraction of all extinctions are caused not by a primary perturbation but instead by the propagation of a cascade," said Motter.
Extinction cascades are often observed following the loss of a key species within an ecosystem. As the system changes to compensate for the loss, availability of food, territory and other resources to each of the remaining members can fluctuate wildly, creating a boom-or-bust environment that can lead to even more extinctions. According to the study, more than 70 percent of these extinctions are preventable, assuming that the system can be brought into balance using only available resources--no new factors may be introduced.
Motter explained further, "We find that extinction cascades can often be mitigated by suppressing--rather than enhancing--the populations of specific species. In numerous cases, it is predicted that even the proactive removal of a species that would otherwise be extinct by a cascade can prevent the extinction of other species."
The finding may seem counterintuitive to conservationists because the compensatory actions seem to inflict further damage to the system. However, when the entire ecosystem is considered, the effect is beneficial. This news holds promise for those charged with maintaining Earth's biodiversity and natural resources--the health of which can counteract many of the causes of climate change, and some man-made disasters such as the Gulf of Mexico oil spill.
The dodo bird, Raphus cucullatus, is one example of extinction due to human activity. The dodo was a large, flightless bird that became extinct in the 1600s. It is likely that a combination of factors including hunting, loss of habitat, and perhaps even a flash flood, stressed the ecosystem on the island of Mauritius, home of the dodo. Some researchers think that human introduction of non-native species, such as dogs, pigs, cats and rats to the island, is what ultimately lead to the demise of the dodo.
In any case, in the future, it may be possible to avoid extinction of some species in stressed ecosystems by applying the new method of analysis developed by Motter.
The goal of this project, funded by the National Science Foundation's Division of Mathematical Sciences, is to develop mathematical methods to study dynamical processes in complex networks. Although the specific application mentioned here may be useful in management of ecosystems, the mathematical foundation underlying the analysis is much more universal. The broad concept is innovative in the area of complex networks because it concludes that large-scale failures can be avoided by focusing on preventing the waves of failure that follow the initial event.
This approach could be used to stabilize a wide array of complex networks. It can apply to biochemical networks in order to slow or stop progression of diseases caused by variations inside individual cells. It can also be used to manage technological networks such as the smart grid to prevent blackouts. It can even apply to regulation of complicated financial networks by identifying key factors in the early stages of a financial downturn, which, when met with human intervention, could potentially save billions of dollars.
The world is a complicated place that gets even trickier when trying to mathematically explain a complex network, especially when the network evolves within an environment that is itself changing. But, Motter says his mathematical model is promising for the study of changing environments.
"Uncertainty itself is not a problem," he quipped. "The problem comes when you cannot estimate uncertainty."
-NSF-
Media Contacts
Lisa Van Pay, NSF, (703) 292-8796, email: lvanpay@nsf.gov
Program Contacts
Henry A. Warchall, NSF, (703) 292-4861, email: hwarchal@nsf.gov
Principal Investigators
Adilson Motter, Northwestern University, (847) 491-4611, email: motter@northwestern.edu
The U.S. National Science Foundation propels the nation forward by advancing fundamental research in all fields of science and engineering. NSF supports research and people by providing facilities, instruments and funding to support their ingenuity and sustain the U.S. as a global leader in research and innovation. With a fiscal year 2023 budget of $9.5 billion, NSF funds reach all 50 states through grants to nearly 2,000 colleges, universities and institutions. Each year, NSF receives more than 40,000 competitive proposals and makes about 11,000 new awards. Those awards include support for cooperative research with industry, Arctic and Antarctic research and operations, and U.S. participation in international scientific efforts.
Connect with us online
NSF website: nsf.gov
NSF News: nsf.gov/news
For News Media: nsf.gov/news/newsroom
Statistics: nsf.gov/statistics/
Awards database: nsf.gov/awardsearch/
Follow us on social
Twitter: twitter.com/NSF
Facebook: facebook.com/US.NSF
Instagram: instagram.com/nsfgov


