News Release 09-122
Global Warming Can Impact Monsoons and Lower Crop Production
New research shows abrupt climate change over 14,000 years ago associated with a shift in monsoon patterns and a decline in vegetation growth
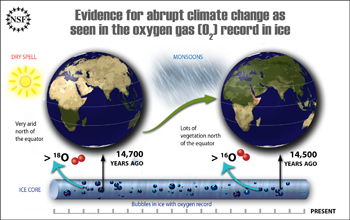
Oxygen gas in ice cores has shown evidence for abrupt climate change.
June 11, 2009
This material is available primarily for archival purposes. Telephone numbers or other contact information may be out of date; please see current contact information at media contacts.
When the climate warmed relatively quickly about 14,700 years ago, seasonal monsoons moved northward. Prior to that, the monsoons were dropping more rain on the Earth's oceans at the expense of tropical areas, according to climate researchers.
In an article to be published in the June 12 issue of the journal Science, researchers from the Desert Research Institute in Nevada, the Scripps Institution of Oceanography and Oregon State University present their findings after comparing oxygen isotopes in air that was captured in ice cores and previously published data from ancient stalagmites found in caves. The research was supported by the National Science Foundation.
The ice cores, gathered from different locations in Antarctica and Greenland, contain air bubbles that were trapped as the ice formed over tens of thousands of years. By measuring the amount of certain oxygen isotopes in those air bubbles, the researchers were able to determine patterns in vegetation growth worldwide over that same span of time.
The researchers found that beginning about 14,700 years ago, the mixture of oxygen isotopes began to change in a way that suggests more vegetation growth, and this process continued for at least 200 years. The researchers then compared these findings with data from an earlier study that determined the amount of rainfall that fell in China over many millennia by examining stalagmites in caves. They discovered that this period of low vegetation growth corresponded with a time of reduced monsoon rainfall.
By climate standards, the researchers say, this shift happened abruptly over a few decades. They also caution that observations of past climate events may not be able predict future conditions. Given the vital roll that monsoons play in sustaining billions of people, however, this connection between climate change and monsoon patterns may be an ominous sign of what climate change in the 21st century may bring.
-NSF-
-
The research appears in the June 12, 2009 edition of the journal Science.
Credit and Larger Version
Media Contacts
Dana W. Cruikshank, NSF, (703) 292-7738, email: dcruiksh@nsf.gov
The U.S. National Science Foundation propels the nation forward by advancing fundamental research in all fields of science and engineering. NSF supports research and people by providing facilities, instruments and funding to support their ingenuity and sustain the U.S. as a global leader in research and innovation. With a fiscal year 2023 budget of $9.5 billion, NSF funds reach all 50 states through grants to nearly 2,000 colleges, universities and institutions. Each year, NSF receives more than 40,000 competitive proposals and makes about 11,000 new awards. Those awards include support for cooperative research with industry, Arctic and Antarctic research and operations, and U.S. participation in international scientific efforts.
Connect with us online
NSF website: nsf.gov
NSF News: nsf.gov/news
For News Media: nsf.gov/news/newsroom
Statistics: nsf.gov/statistics/
Awards database: nsf.gov/awardsearch/
Follow us on social
Twitter: twitter.com/NSF
Facebook: facebook.com/US.NSF
Instagram: instagram.com/nsfgov



