Multimedia Gallery
Microbial Electrolysis Cell
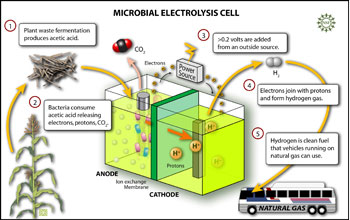
Researchers have designed a microbial electrolysis cell in which bacteria break up acetic acid (a product of plant waste fermentation) to produce hydrogen gas with a very small electric input from an outside source. Hydrogen can then be used for fuel cells or as a fuel additive in vehicles that now run on natural gas.
This image accompanied NSF press release, "Microbes Churn Out Hydrogen at Record Rate."
Credit: Zina Deretsky, National Science Foundation
Images and other media in the National Science Foundation Multimedia Gallery are available for use in print and electronic material by NSF employees, members of the media, university staff, teachers and the general public. All media in the gallery are intended for personal, educational and nonprofit/non-commercial use only.
Images credited to the National Science Foundation, a federal agency, are in the public domain. The images were created by employees of the United States Government as part of their official duties or prepared by contractors as "works for hire" for NSF. You may freely use NSF-credited images and, at your discretion, credit NSF with a "Courtesy: National Science Foundation" notation.
Additional information about general usage can be found in Conditions.
Also Available:
Download the high-resolution JPG version of the image. (511 KB)
Use your mouse to right-click (Mac users may need to Ctrl-click) the link above and choose the option that will save the file or target to your computer.