Multimedia Gallery
Differences in Quakes
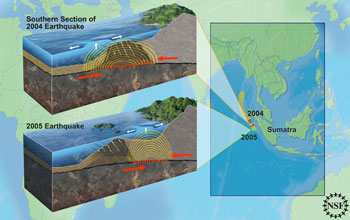
Researchers found differences between the rocks in the regions where the 2004 and 2005 Sumatran earthquakes occurred. In the southern part of the region where the 2004 earthquake occurred, the earthquake rupture began closer to shore and did not reach as far seaward. Comparatively, the 2005 earthquake ruptured farther seaward beneath a thick wedge of compacted sedimentary rocks. These differences help explain why the 2004 earthquake and ensuing tsunami were more severe than subsequent events in 2005.
This image accompanied NSF press release
"New Findings Indicate Sediment Composition Affected the Strength of Sumatran Earthquake."
Credit: Nicolle Rager Fuller, National Science Foundation
Images and other media in the National Science Foundation Multimedia Gallery are available for use in print and electronic material by NSF employees, members of the media, university staff, teachers and the general public. All media in the gallery are intended for personal, educational and nonprofit/non-commercial use only.
Images credited to the National Science Foundation, a federal agency, are in the public domain. The images were created by employees of the United States Government as part of their official duties or prepared by contractors as "works for hire" for NSF. You may freely use NSF-credited images and, at your discretion, credit NSF with a "Courtesy: National Science Foundation" notation.
Additional information about general usage can be found in Conditions.
Also Available:
Download the high-resolution JPG version of the image. (455 KB)
Use your mouse to right-click (Mac users may need to Ctrl-click) the link above and choose the option that will save the file or target to your computer.