News From the Field
Supercomputer predicts optical properties of complex hybrid materials
October 8, 2018
This material is available primarily for archival purposes. Telephone numbers or other contact information may be out of date; please see current contact information at media contacts.
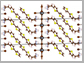
Materials scientists at Duke University computationally predicted the electrical and optical properties of semiconductors made from extended organic molecules sandwiched by inorganic structures. These types of so-called layered "hybrid organic-inorganic perovskites" -- or HOIPs -- are popular targets for light-based devices such as solar cells and light-emitting diodes. The ability to build accurate models of these materials atom-by-atom will allow researchers to explore new material designs.Full StorySource
Duke University
The U.S. National Science Foundation propels the nation forward by advancing fundamental research in all fields of science and engineering. NSF supports research and people by providing facilities, instruments and funding to support their ingenuity and sustain the U.S. as a global leader in research and innovation. With a fiscal year 2023 budget of $9.5 billion, NSF funds reach all 50 states through grants to nearly 2,000 colleges, universities and institutions. Each year, NSF receives more than 40,000 competitive proposals and makes about 11,000 new awards. Those awards include support for cooperative research with industry, Arctic and Antarctic research and operations, and U.S. participation in international scientific efforts.
Connect with us online
NSF website: nsf.gov
NSF News: nsf.gov/news
For News Media: nsf.gov/news/newsroom
Statistics: nsf.gov/statistics/
Awards database: nsf.gov/awardsearch/
Follow us on social
Twitter: twitter.com/NSF
Facebook: facebook.com/US.NSF
Instagram: instagram.com/nsfgov