All Images
News Release 05-164
Marine Microorganism Suspected to Play Role in Global Carbon and Nitrogen Cycles
Scientists successfully grow "dwarf belonging to the sea" in laboratory
This material is available primarily for archival purposes. Telephone numbers or other contact information may be out of date; please see current contact information at media contacts.

Researchers discovered that a single-celled marine microorganism of the Archaea kingdom may play an important role in global nitrogen and carbon cycling. The new finding was evident after scientists determined what nutrients were needed to keep the organism growing in the laboratory.
Credit: Illustration created by Nicolle Rager Fuller, National Science Foundation. Micrograph image provided by M. Koenneke and D. Stahl, University of Washington.
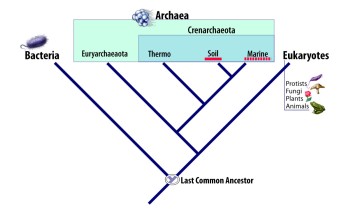
By studying genetic characteristics scientists currently divide all living organisms into three kingdoms named bacteria, archaea and eukaryotes when they depict the "Tree of Life."
Credit: Nicolle Rager Fuller, National Science Foundation
Download the high-resolution JPG version of the image. (80 KB)
Use your mouse to right-click (Mac users may need to Ctrl-click) the link above and choose the option that will save the file or target to your computer.


