Get OLPA Email Updates
The Office of Legislative and Public Affairs (OLPA) communicates the U.S. National Science Foundation's activities, programs, research results and policies.
OLPA uses a variety of approaches to engage with the public, Congress, the news media, state and local governments, other federal agencies, research and education communities and internal NSF offices and directorates.
OLPA branches

Government Affairs
The Government Affairs branch is the principal point of contact between Congress and NSF, coordinating requests for information and ensuring timely responses to congressionally mandated reports and correspondence. The branch also arranges meetings with congressional members and staff, coordinates NSF officials' appearances at congressional hearings and arranges site visits to NSF-supported facilities.
Visit the NSF and Congress webpage for information on the latest budget request to Congress, congressional testimonies and summaries, major legislation and program awards by state/district.

Public and Media Affairs
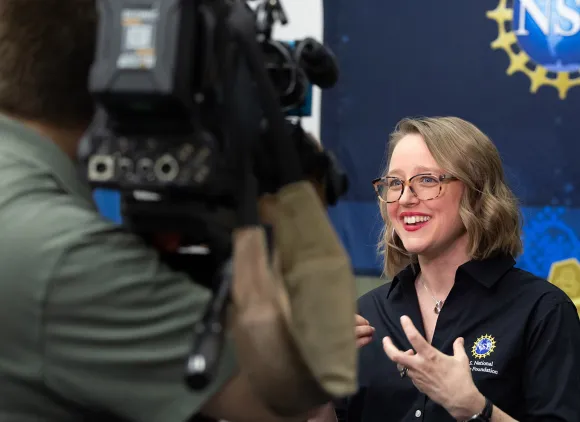
The Public and Media Affairs branch is responsible for communications planning and strategy, media relations, content development and outreach.
For media inquiries, please call (703) 292-7090 or email media@nsf.gov.
Creative Services
The Creative Services branch leads NSF's digital engagement and visual brand management strategy. The branch creates digital content in collaboration with NSF directorates and offices and shares it on social media, NSF.gov and radio and television stations nationwide.
Please email nsfbranding@nsf.gov if you have questions about NSF branding or logo usage.

Business Operations
The Business Operations branch supports OLPA's day-to-day operations. It manages and oversees the office's contracts, budget formulation and execution, administrative functions, human capital management and internal communications.