TIP Investment Explorer user guide
The U.S. National Science Foundation Directorate for Technology, Innovation and Partnerships (NSF TIP) launched the TIP Investment Explorer, featuring NSF award data in map and impact views, to showcase the scale and impact of NSF TIP's investments in key technology areas across the nation. The TIP Investment Explorer uses Elsevier's Pure platform, a research information management system that leverages open access data repositories to show the organizations – including startups and small businesses – and the principal investigators who are advancing the TIP portfolio. The tool illustrates the impact of NSF's investments across 10 key technology areas. Data in the visualization is pulled from the public NSF award search database and categorized into key technology areas with machine learning.
Through the TIP Investment Explorer, NSF invites users to access a comprehensive one-stop hub showcasing the outcomes and impacts generated by TIP's investments over time. Incrementally, TIP will add more features and data to the platform.
About the data
- The TIP Investment Explorer contains data from research and development awards and contracts that were active starting in Fiscal Year 2022 to present. Data on awards are drawn from NSF's public award search and are updated daily, with a two-day delay from the award publication date.
- Subawardee data are drawn from USASpending.
- Organization Type data for both awardee and subawardee organizations are drawn from Sam.gov.
- Researcher profile information is provided by Elsevier. New profiles are updated weekly.
- Impact View data is updated quarterly.
TIP Investment Explorer
Quick Start Guide
Awards by Key Technology Area
Awards by Programs
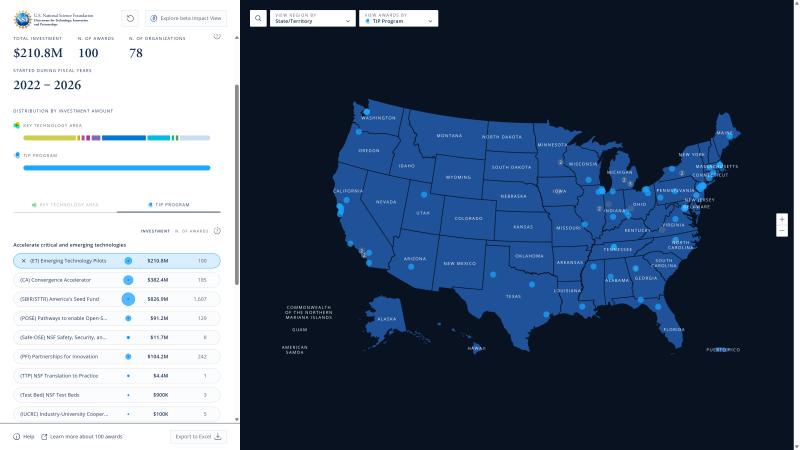
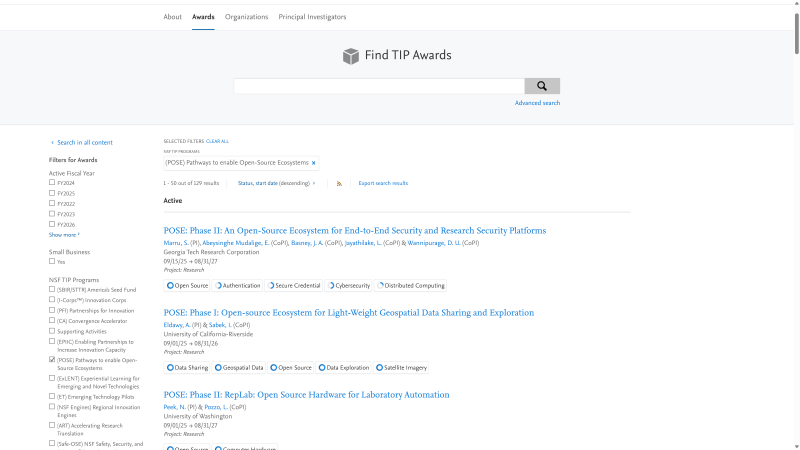
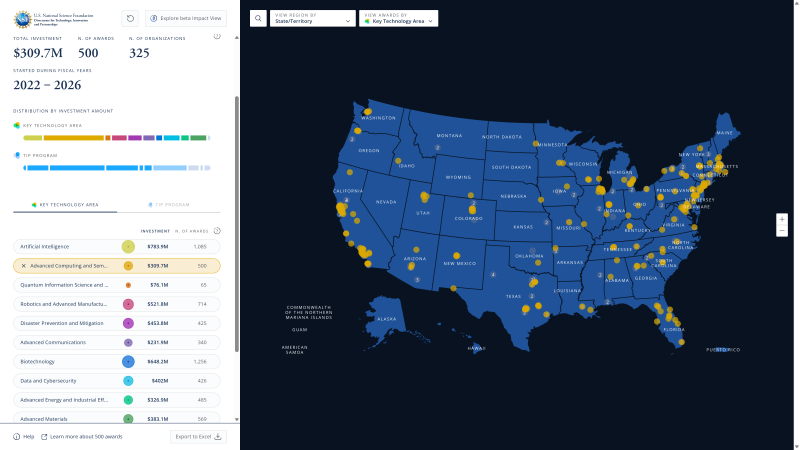
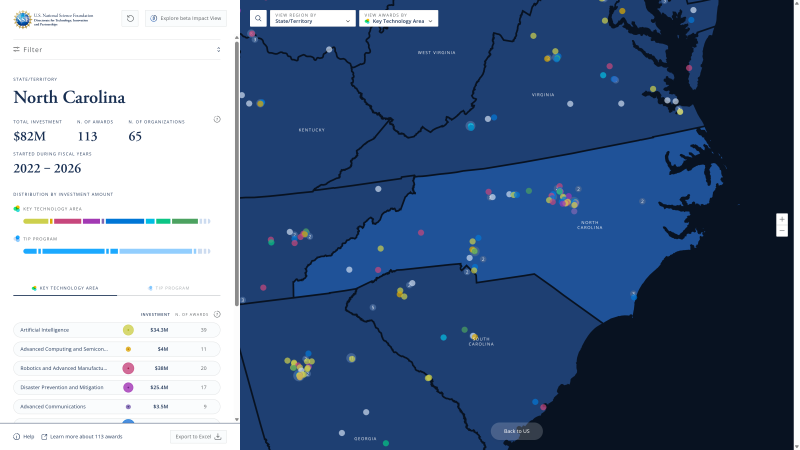
- The map of TIP investments allows users to filter awards by Active Fiscal Year, Start Fiscal Year, Current Active Status, Active Program, and Established Program to Stimulate Competitive Research (EPSCoR) Status.
- Awards and contracts may be tagged with multiple technology areas, and the number displayed includes duplicates.
- The investment/funding amount is Total Intended Award Amount.
- Displayed dollar amount should not be used to calculate the budget. Some awards are continuing grants, and it may appear as though NSF is investing more or less in a given year. Please contact tip@ nsf.gov for more information about the budget.
Map symbols explained
- Each point on the map represents an organization.
- Filled circles represent one organization receiving a TIP award/contract.
- Hollow circles represent one organization receiving a subaward.
- Clusters with numbers represent the number of awards, contracts and subawards received by an organization.
| Mark Type | Meaning |
| One organization receiving an award or research contract. | |
| One organization receiving a subaward. | |
| One organization receiving two or more awards, contracts or subawards. |
How to view organization and award details on the map
- Hover over a map point to view details, including organization name, organization type, award or contract title and award or subaward designation.
- If an organization has one award, additional information like award ID, investment amount and principal investigator appears on hover.
- N. of Awards in the side panel reflects the total awards and contracts for the filters applied. This total does not include subawards.
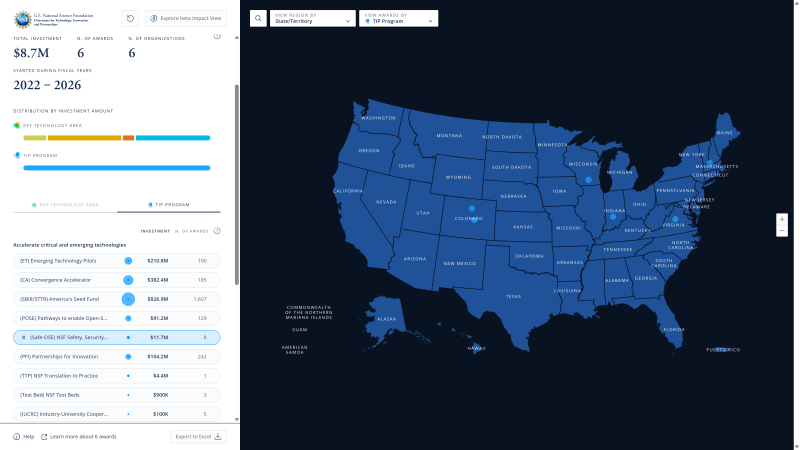
The TIP Impact View dashboard displays the economic impact of TIP programs across the U.S. Users can analyze impact by Key Technology Area or TIP program. Results are displayed in a Sankey graph showing the flow of investments and outcomes.
Key metrics include startups launched, jobs created and follow-on funding. These data points are summarized alongside total awards and investment amounts. Additional panels provide program details, funding notes and interactive options to explore the data further. The TIP Investment Explorer includes NSF investments in NSF Innovation Corps (I-Corps™) national teams and America's Seed Fund, powered by NSF, also known as the Small Business Innovation Research/Small Business Technology Transfer (SBIR/STTR) programs from FY 2012-2024. Data will be updated quarterly, and additional programs will be added over time.
To export results from the map, click the Export to Excel button located at the bottom of the left sidebar.
Note: The N. Of Awards in the side panel may differ from the number of rows in the exported Excel file because the export includes subawards.
What's included in the Excel export
- Award/contract ID
- Award/contract title
- Award/contract abstract
- Organization and lead/subawardee designation
- Total Investment (for prime and subawardees)
- NSF award URL
- Award start and end date
- PI and Co-PI names
- State, congressional district, county and Core-Based Statistical Area (CBSA)
- TIP program(s) award is part of
- Key Technology Area(s)
- Program status (active/inactive)
- NSF EPSCoR
- Portal URL
Searching by TIP program can be done on the map or in the database.
- On the map: To search for one or more TIP programs on the map, select TIP Program in the left sidebar, then choose one or more TIP Program labels below.
- To further refine results by KTA within a TIP Program, select a TIP Program label in the left sidebar, then click on Key Technology Area and choose a KTA label.
- In the database portal: navigate to the Awards page, then choose one or more TIP Programs from the TIP Programs filter.
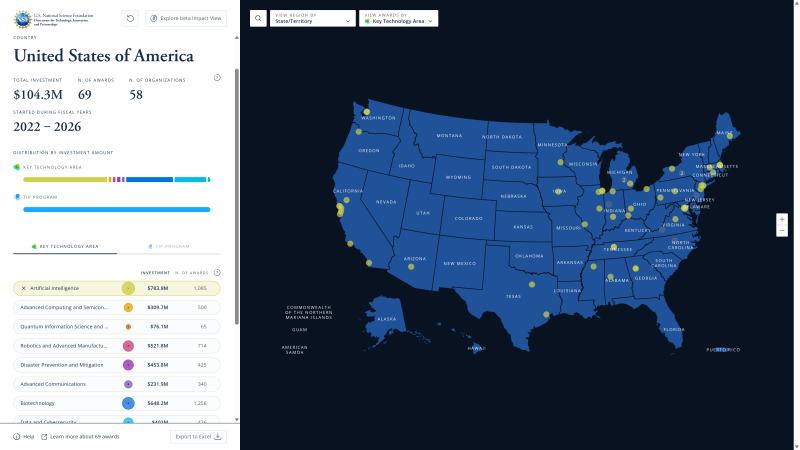
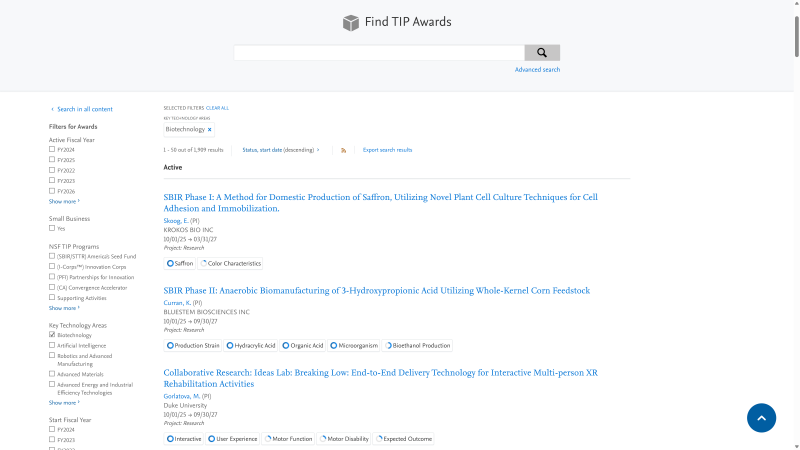
Searching by KTA can be done on the map or on the database portal.
- On the Map: Select Key Technology Area in the left sidebar and then choose one or more KTA labels below.
- To further refine results by TIP Program within a KTA, select a KTA label in the left sidebar, then click on TIP Program and choose a TIP program.
- In the database portal: Navigate to the Awards page, then choose one or more KTAs from the Key Technology Areas filter.
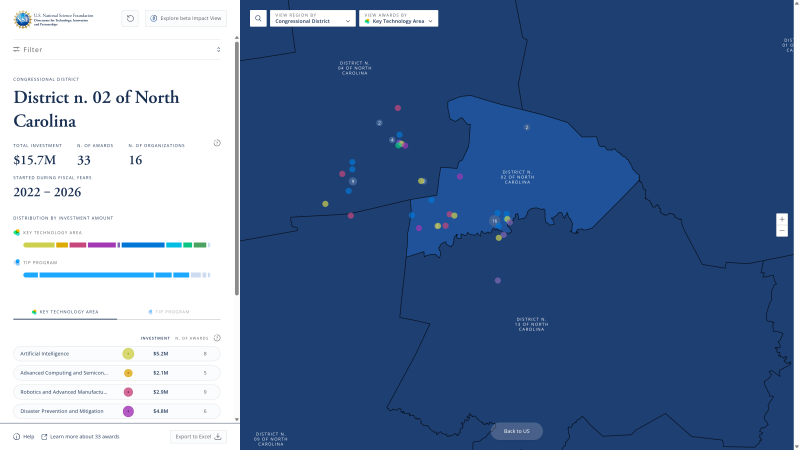
Searching for awards by state, congressional district, core-based statistical area, or county is best achieved through the map. After selecting a geographic area, the total NSF investment amount and bar charts showing the investment distribution by TIP program will update dynamically in the left sidebar.
- To view awards by state, choose a state from the map.
- To further refine results by congressional district, select Congressional District from the View Region By dropdown at the top of the page, then choose a congressional district on the map.
- To view results by county or CBSA, select a state, then select County or Core-Based Statistical Area from the View Region By dropdown at the top of the page. Then, choose a county or CBSA on the map.
- Another way to refine results by geographic area is through the search bar in the upper left corner of the map area.
- Enter a state, territory, county or CBSA name in the search bar, then choose the desired area from the dropdown menu.
- To return to the default map view, select the Back to U.S. button at the bottom of the map view.
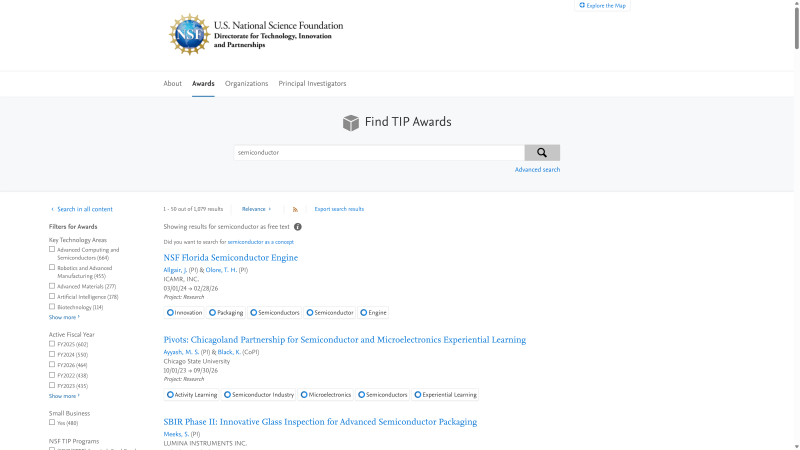
Searching by concept or keyword must be done in the database portal.
Free text search
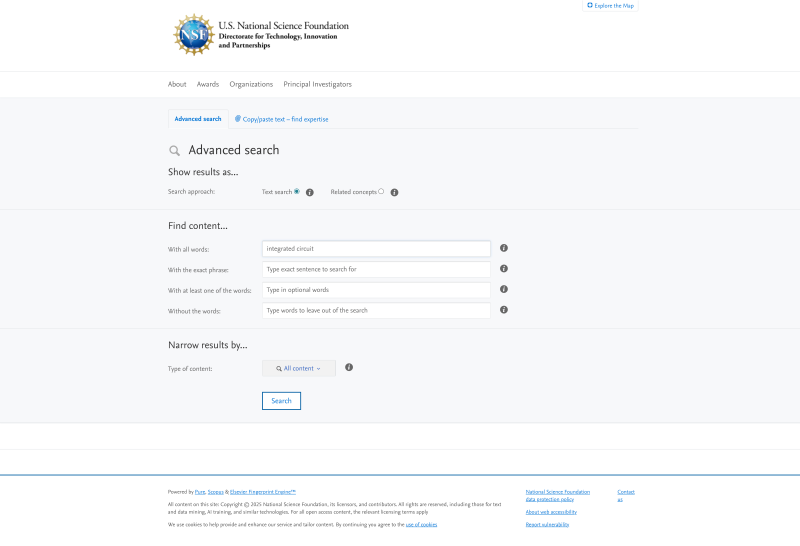
Concept Search
Select Advanced Search below the search bar on the Awards page, then select "Related concepts" for the search approach. Enter keywords in one of the Find Content search bars, then click Search.
Ten Key Technology Areas (KTAs are crucial for the nation's economic and national security. TIP utilizes state-of-the-art machine learning to label awards with the corresponding KTA, ensuring a clear association between TIP awards and respective KTA. TIP has further broken down the KTA into 47 Technology Foci to better sort and filter awards.
KTA1 — Artificial intelligence, machine learning (ML), autonomy and related advances
- KTA1.1 Artificial intelligence (excluding ML)
- KTA1.2 Machine learning (ML)
- KTA1.3 Machine learning training data
- KTA1.4 Autonomy
KTA2 — High-performance computing; semiconductors, and advanced computer hardware and software
- KTA2.1 High-performance computing (HPC)
- KTA2.2 Advanced computer hardware
- KTA2.3 Advanced computer software
- KTA2.4 Semiconductors
KTA3 — Quantum information science and technology
- KTA3.1 Quantum computing algorithms and software
- KTA3.2 Quantum computing hardware
- KTA3.3 Quantum communications and networking
- KTA3.4 Quantum sensing
- KTA3.5 Quantum device components and manufacturing methods
KTA4 — Robotics, automation and advanced manufacturing
- KTA4.1 Robotics
- KTA4.2 Automation
- KTA4.3 Advanced manufacturing (excluding biomanufacturing and semiconductor manufacturing)
KTA5 — Natural and anthropogenic disaster prevention or mitigation
- KTA5.1 Natural disaster prevention and mitigation (excluding climate resilience)
- KTA5.2 Climate resilience
- KTA5.3 Anthropogenic disaster prevention and mitigation (excluding pandemics)
- KTA5.4 Pandemic prevention and response
KTA6 — Advanced communications technology and immersive technology
- KTA6.1 Wireless communication — terrestrial and space
- KTA6.2 Wired and fiber communication
- KTA6.3 Spectrum management
- KTA6.4 Communications and network security
- KTA6.5 Internetworking
- KTA6.6 Immersive technology and edge devices
KTA7 — Biotechnology, medical technology, genomics and synthetic biology
- KTA7.1 Biotechnology — other than synthetic biology
- KTA7.2 Medical technology
- KTA7.3 Genomics and bioinformatics
- KTA7.4 Synthetic biology
- KTA7.5 Biomanufacturing
KTA8 — Data storage, data management, distributed ledger technologies and cybersecurity, including biometrics
- KTA8.1 Data storage
- KTA8.2 Data management and databases
- KTA8.3 Data privacy
- KTA8.4 Distributed ledger technologies
- KTA8.5 Cybersecurity
- KTA8.6 Biometrics
KTA9 — Advanced energy and industrial efficiency technologies, such as batteries and advanced nuclear technologies, including but not limited to, for the purposes of electric generation (consistent with section 15 of the "National Science Foundation Act of 1950" (42 U.S.C. 1874)
- KTA9.1 Advanced batteries and energy storage technologies
- KTA9.2 Advanced energy generation technologies
- KTA9.3 Advanced transmission and distribution systems
- KTA9.4 Carbon management technologies
- KTA9.5 Advanced nuclear technologies
- KTA9.6 Industrial efficiency technologies
KTA10 — Advanced materials science, including composite 2D materials, other next-generation materials and related manufacturing technologies
- KTA10.1 Composites (excluding 2D materials)
- KTA10.2 2D materials
- KTA10.3 Other next-generation materials
- KTA10.4 Related manufacturing technologies
A distinguishing feature of the Pure platform is the Elsevier Fingerprint Engine (Engine), which mines the text of public scientific documents, such as publication abstracts, funding announcements, patents and awards, to create an index of weighted terms that defines the text-fingerprint visualization.
Indexing
By compiling and comparing fingerprint indexes, the Engine enables institutions to look beyond metadata and find valuable connections among people, publications, funding opportunities and ideas. The Engine powers many Elsevier solutions, including Pure and Expert Lookup, an Elsevier tool for finding reviewers, to inform decision-making.
Thesauri
Using a wide collection of thesauri, the Engine can support applications pertaining to multiple subject areas. This allows Elsevier to develop solutions for researchers in the life sciences, engineering, Earth and environmental sciences, arts and humanities, social sciences, mathematics, agriculture and more.
How it works
The Elsevier Fingerprint Engine creates indexes in the following steps:
- The Engine applies a variety of natural language processing techniques to mine the text of scientific documents, including publication abstracts, funding announcements, awards, project summaries, patents, proposals, applications and other sources.
- The Engine identifies key concepts that define the text using thesauri spanning major disciplines.
- The Engine creates an index of weighted terms that defines the text, known as a Fingerprint index
Active FY
The federal government fiscal year(s) during which an organization receives NSF funding for an award or contract. An award beginning Oct. 1, 2025, and ending April 1, 2027, has the following active FYs: FY 2026, FY 2027.
Award or contract status
Indicates whether the organization has received NSF funding. An organization can have multiple awards or contracts with NSF.
- Active — the organization is receiving NSF funds or is operating under a "no-cost extension" to complete the project.
- Finished — the organization is no longer receiving NSF funding, and the award has been officially closed out or "closed" in NSF systems.
- Not started — the award has been made, but the organization cannot collect NSF funding until a set start date is shown for each award.
Congressional district
An area that elects a member of the U.S. House of Representatives.
Core-based statistical area (CBSA)
Core-based statistical areas (CBSAs) is the collective term used to refer to metropolitan statistical areas and micropolitan statistical areas, which are delineated by the Office of Management and Budget (OMB). OMB generally defines a CBSA as an area that contains a central county that has a substantial urban population, along with any adjacent communities that have a high level of integration with the central county. In 2020, OMB defined CBSAs to consist of a county or multiple counties (or other equivalent entities) that contain a core urban area with a minimum population of 10,000.
County
Counties are the primary political and administrative divisions of States.
Emergent technologies
Rapidly developing technology areas that are not yet widely implemented but show strong transformative potential.
Exploratory activities
Early-stage efforts that assess new concepts and inform future research and technology development.
Fiscal year (FY)
The federal government's fiscal year runs from Oct. 1 to Sept. 30. For example, FY 2023 is Oct. 1, 2022, to Sept. 30, 2023.
Follow-on funding
Additional funding an organization receives after the initial NSF award.
- Public: funding from government sources.
- Private: funding from investors and other organizations.
Jobs created
Employment opportunities created as a result of NSF investment.
Metropolitan statistical areas
Metropolitan statistical areas have at least one urbanized area of 50,000 or more population, plus adjacent territory that has a high degree of social and economic integration with the core as measured by commuting ties.
Micropolitan statistical areas
Micropolitan statistical areas have at least one urban cluster of at least 10,000 but less than 50,000 population, plus adjacent territory that has a high degree of social and economic integration with the core as measured by commuting ties.
NSF EPSCoR
The NSF Established Program to Stimulate Competitive Research (NSF EPSCoR) program pursues a mission to enhance the research competitiveness of targeted jurisdictions (state, territory or commonwealth) by strengthening science, technology, engineering and mathematics capacity and capability through a diverse portfolio of investments from talent development to local infrastructure. For more information about EPSCoR, visit https://www.nsf.gov/funding/initiatives/epscor
Program status
- On (active): shows active funding opportunities only
- Off: shows active and archived (expired) funding opportunities
Scaling technology capacity
Activities that build the infrastructure and translational pathways needed to mature and deploy technology at scale.
Start FY
When the award began, in terms of the federal government's fiscal year. For example, the start FY for an award beginning Oct. 1, 2025, is FY 2026.
Startups launched
New businesses opened as a result of initial NSF investment.
Subaward
An agreement that a prime recipient makes with another entity to perform a portion of their award.
The TIP Investment Explorer is configured on the Elsevier Pure platform, which is not custom-built and is created and maintained by Elsevier for other clients. Many of Elsevier's features used in this platform have some limitations and cannot be modified at present. These limitations include:
- Categories and filters cannot be adjusted or hidden in the left-hand filter pane. (Note that TIP has added custom filters to help present data.)
- The affiliated organization displayed in a principal investigator's (PI) Pure platform profile is based on the lead institution associated with the award and may differ from the affiliated organization shown in a PI's Scopus profile.
- The "export search" results feature in the database portal is limited to 50 items, and the fields included in the search results export are Rank, Award Name and the URL to the corresponding award (in Pure platform). Fields included in the export cannot be modified or expanded.
- Beta Impact View — The Impact View is currently in beta and only includes SBIR/STTR and the I-Corps National Teams program. Additional programs will be added over time.
- Subaward Visualizations — Some tooltips may make it difficult to view subaward connections clearly. This functionality is a work in progress.
Please note that not all functionality of the TIP Investment Explorer is final. Additional features will be added in the future.
Contact Us
Share your feedback with TIP by emailing tip@nsf.gov.