News Release 10-065
Scientists Discover Underwater Asphalt Volcanoes
Impressive landmarks hidden for 40,000 years rise from sea-floor
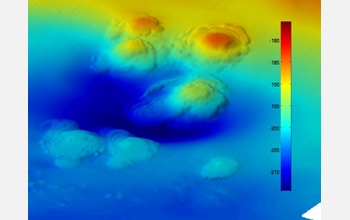
High-resolution bathymetry shows extinct asphalt volcanoes on the sea-floor off California.
April 25, 2010
This material is available primarily for archival purposes. Telephone numbers or other contact information may be out of date; please see current contact information at media contacts.
About 10 miles off the Santa Barbara coast, at the bottom of the Santa Barbara Channel, a series of impressive landmarks rise from the sea floor.
They've been there for 40,000 years, but have remained hidden in the murky depths of the Pacific Ocean--until now.
They're called asphalt volcanoes.
Scientists funded by the National Science Foundation (NSF) and affiliated with the University of California at Santa Barbara (UCSB), the Woods Hole Oceanographic Institution (WHOI), University of California at Davis, University of Sydney and University of Rhode Island, have identified the series of unusual volcanoes.
The largest of these undersea Ice Age domes lies at a depth of 700 feet (220 meters), too deep for scuba diving, which explains why the volcanoes have never before been spotted by humans, says Don Rice, director of NSF's Chemical Oceanography Program, which funded the research.
"They're larger than a football-field-long and as tall as a six-story building," says David Valentine, a geoscientist at UCSB and the lead author of a paper published on-line this week in the journal Nature Geoscience. "They're massive features, and are made completely out of asphalt."
Valentine and colleagues first viewed the volcanoes during a 2007 dive on the research submersible Alvin. Valentine credits Ed Keller, an earth scientist at UCSB, with guiding him and colleagues to the site.
"Ed had looked at some bathymetry [sea floor topography] studies conducted in the 1990s and noted some very unusual features," Valentine says.
Based on Keller's research, Valentine and other scientists took Alvin into the area in 2007 and discovered the source of the mystery.
Using the sub's robotic arm, the researchers broke off samples and brought them to labs at UCSB and WHOI for testing.
In 2009, Valentine and colleagues made two more dives to the area in Alvin. They also conducted a detailed survey of the area using an autonomous underwater vehicle, Sentry, which takes photos as it glides about nine feet above the ocean floor.
"When you 'fly' Sentry over the sea floor, you can see all of the cracking of the asphalt and flow features," says Valentine. "All the textures are visible of a once-flowing liquid that has solidified in place.
"That's one of the reasons we're calling them volcanoes, because they have so many features that are indicative of a lava flow."
Tests showed that these aren't your typical lava volcanoes, however, found in Hawaii and elsewhere around the Pacific Rim.
Using a mass spectrometer, carbon dating, microscopic fossils, and comprehensive, two-dimensional gas chromatography, the scientists determined that the structures are asphalt. They were formed when petroleum flowed from the sea-floor about 30,000-40,000 years ago.
Chris Reddy, a scientist at WHOI and a co-author of the paper, says that "the volcanoes underscore a little-known fact: half the oil that enters the coastal environment is from natural oil seeps like the ones off the coast of California."
The researchers also determined that the volcanoes were at one time a prolific source of methane, a greenhouse gas.
The two largest volcanoes are about a kilometer apart and have pits or depressions surrounding them. These pits, according to Valentine, are signs of "methane gas bubbling from the sub-surface."
That's not surprising, he says, considering how much petroleum was flowing there in the past.
"They were spewing out a lot of petroleum, but also lots of natural gas," he says, "which you tend to get when you have petroleum seepage in this area."
The discovery that vast amounts of methane once emanated from the volcanoes caused the scientists to wonder if there might have been an environmental impact on the area during the Ice Age.
"It became a dead zone," says Valentine. "We're hypothesizing that these features may have been a major contributor to those events."
While the volcanoes have been dormant for thousands of years, the 2009 Alvin dive revealed a few spots where gas was still bubbling.
"We think it's residual gas," says Valentine, who added that the amount of gas is so small it's harmless, and never reaches the surface.
Other co-authors of the paper are Christopher Farwell, Sarah C. Bagby, Brian A. Clark, and Morgan Soloway, all of UCSB; Robert K. Nelson, Dana Yoerger, and Richard Camilli of WHOI; Tessa M. Hill, UC Davis; Oscar Pizarro, University of Sydney; and Christopher N. Roman, University of Rhode Island.
-NSF-
-
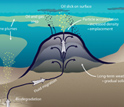
Diagram showing formation of an asphalt volcano and associated release of methane and oil.
Credit and Larger Version -
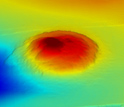
One of the extinct undersea asphalt volcanoes shown with high-resolution bathymetry.
Credit and Larger Version -
A slab from an asphalt volcano discovered on the sea-floor of the Santa Barbara Channel.
Credit and Larger Version -
Photo of Christopher Farwell, Sarah Bagby and David Valentine with a piece of asphalt volcano.
Credit and Larger Version
Media Contacts
Cheryl Dybas, NSF, (703) 292-7734, email: cdybas@nsf.gov
George Foulsham, UCSB, (805) 893-3071, email: george.foulsham@ia.ucsb.edu
The U.S. National Science Foundation propels the nation forward by advancing fundamental research in all fields of science and engineering. NSF supports research and people by providing facilities, instruments and funding to support their ingenuity and sustain the U.S. as a global leader in research and innovation. With a fiscal year 2023 budget of $9.5 billion, NSF funds reach all 50 states through grants to nearly 2,000 colleges, universities and institutions. Each year, NSF receives more than 40,000 competitive proposals and makes about 11,000 new awards. Those awards include support for cooperative research with industry, Arctic and Antarctic research and operations, and U.S. participation in international scientific efforts.
Connect with us online
NSF website: nsf.gov
NSF News: nsf.gov/news
For News Media: nsf.gov/news/newsroom
Statistics: nsf.gov/statistics/
Awards database: nsf.gov/awardsearch/
Follow us on social
Twitter: twitter.com/NSF
Facebook: facebook.com/US.NSF
Instagram: instagram.com/nsfgov